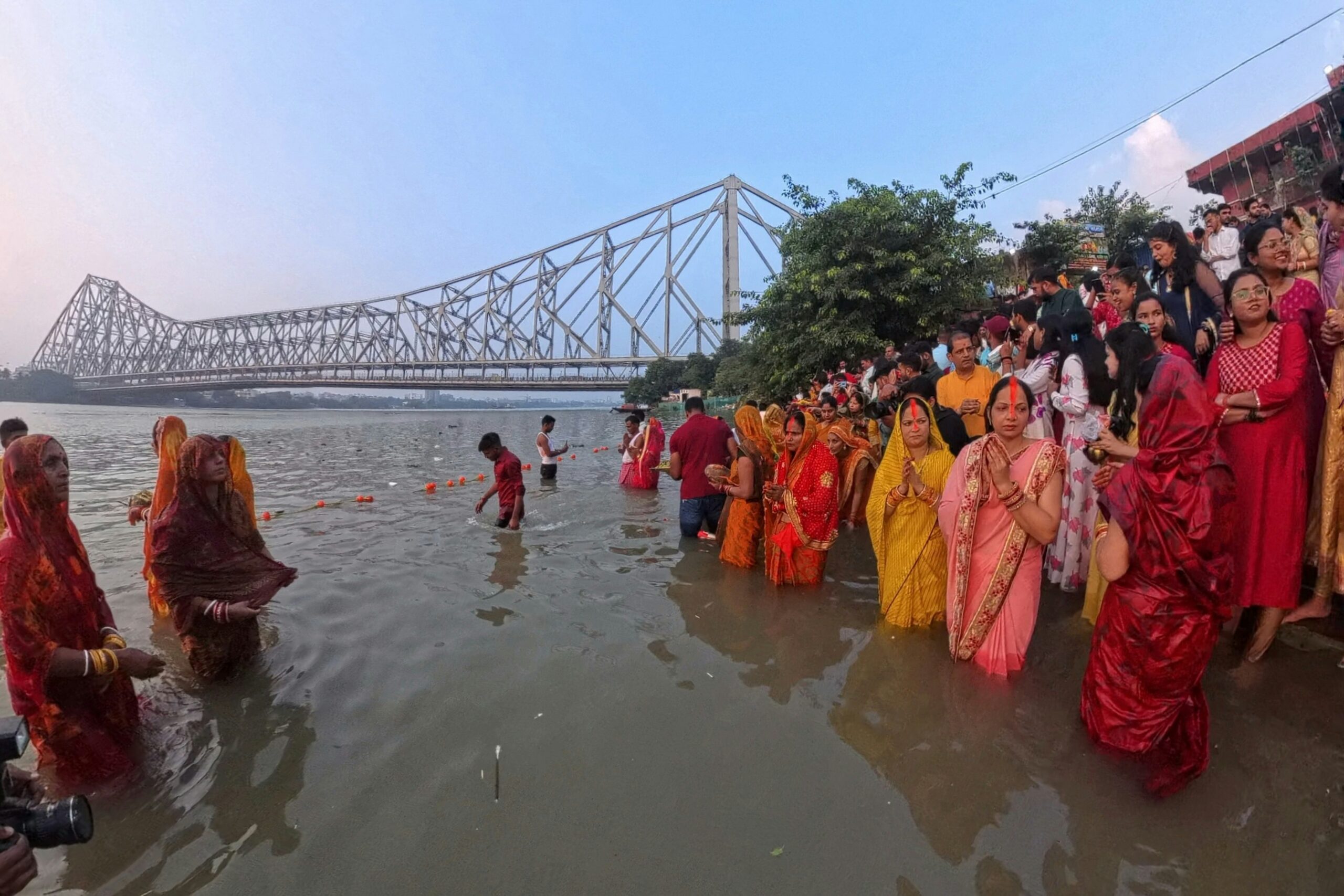
As the sacred waters of the Ganga, revered by millions, ebb to unprecedented lows, a silent crisis unfolds along its banks. Once a roaring lifeline that nourished countless communities and ecosystems, India’s holiest river now faces alarming challenges that threaten not only its flow but also the very fabric of life intertwined with it. From agricultural distress to dwindling fish populations and increasing pollution levels, the implications are vast—and urgent. Join us as we delve deep into this pivotal moment in history, exploring what these low streamflows mean for both people and nature alike. Together, let’s navigate through this complex tapestry of tradition, ecology, and survival in one of the world’s most vital waterways.
Introduction to the Ganga River and its historical significance
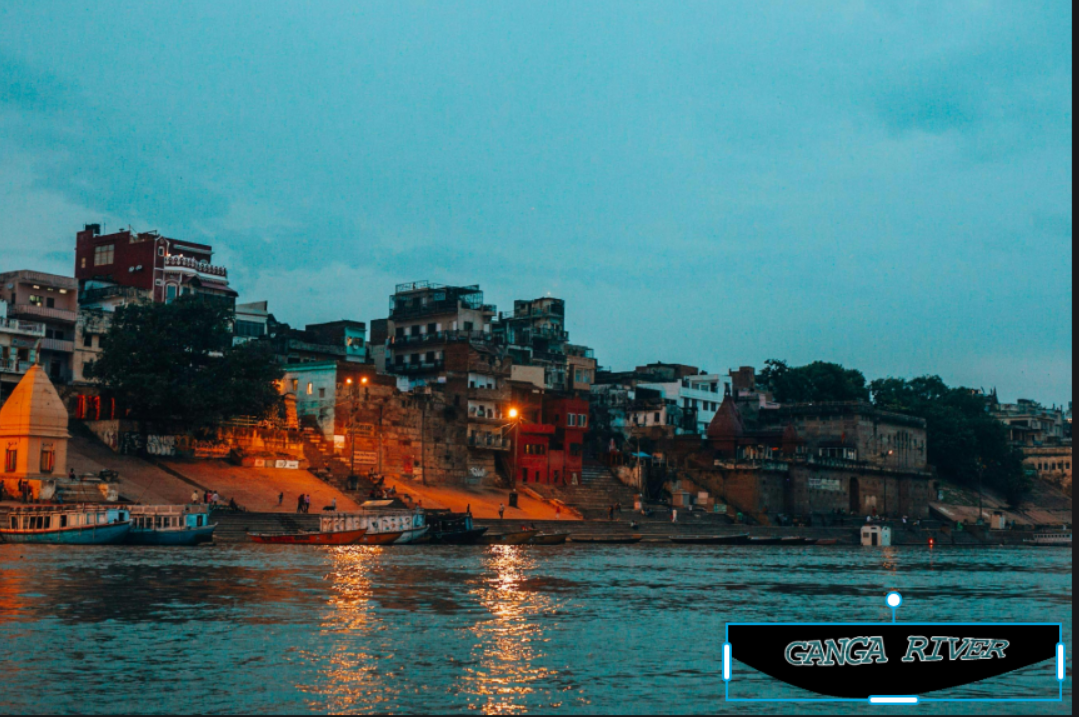
The Ganga River, a sacred lifeline for millions in India, has long been revered not just as a waterway but as an embodiment of culture and spirituality. Stretching over 2,500 kilometers, it weaves through the heart of the subcontinent, nourishing cities and villages alike. Historically significant, this river has witnessed the rise and fall of civilizations while providing sustenance to countless communities along its banks.
However, today’s reality presents a stark contrast to its storied past. The Ganga faces an unprecedented crisis marked by dangerously low streamflow levels that threaten both ecological balance and human livelihoods. As we navigate this pressing issue together—understanding its causes and implications—we uncover why action is imperative for preserving one of India’s most precious resources.
The current crisis: Reasons for low streamflow and the impact on communities
The Ganga River, once a robust lifeline for millions, now faces an alarming decline in streamflow. Several factors contribute to this crisis. Rapid urbanization leads to increased water extraction and pollution, straining the river’s resources.
Moreover, extensive damming projects disrupt natural flow patterns. These infrastructures are vital for irrigation and power generation, but compromise the ecological balance of the river.
Communities that depend on the Ganga face dire consequences. Farmers struggle as fields dry up, lacking sufficient irrigation. Fishermen see dwindling catches affecting their livelihoods and food security.
Additionally, local populations suffer from inadequate access to clean drinking water due to declining river levels. The cultural significance of the Ganga adds another layer; rituals tied to its waters become increasingly challenging as sacred sites experience lower flows.
Examining the role of climate change in the situation
Climate change is a significant factor behind the Ganga River’s unprecedented low streamflow. Rising temperatures have led to altered precipitation patterns across India. This means less rain during critical monsoon months, impacting river levels dramatically.
Glacial melt from the Himalayas also plays a crucial role. As global warming accelerates, glaciers retreat faster than before. This phenomenon reduces the long-term supply of freshwater that feeds into the Ganga.
Moreover, extreme weather events—such as unpredictable droughts and heavy flooding—are becoming more common. These fluctuations disrupt local ecosystems and affect communities reliant on the river for sustenance and livelihood.
The intertwined relationship between climate change and water resources highlights an urgent need for adaptive strategies. Stakeholders must recognize these challenges to formulate effective responses tailored to preserving this vital waterway.
India’s response: Proposed changes to the Ganges water-sharing treaty with Bangladesh
India’s response to the crisis surrounding the Ganga River has been multifaceted, particularly in relation to its water-sharing agreement with Bangladesh. The unprecedentedly low streamflow has raised urgent concerns about equitable access.
One major proposal involves renegotiating aspects of the Ganges Water Sharing Treaty established in 1996. This treaty aimed for a fair distribution but may now be inadequate given current environmental challenges.
The Indian government is exploring options that could enhance cooperation with Bangladesh while ensuring both nations can address their growing water needs. Discussions are likely to focus on adaptive management strategies and enhanced monitoring systems.
Additionally, there’s emphasis on joint initiatives for sustainable water usage and conservation practices along shared riverbanks. Strengthening diplomatic ties through dialogue will be essential as both countries navigate these pressing issues together.
Global implications of the Ganga River crisis
The Ganga River crisis extends far beyond India’s borders. As one of the most important rivers in South Asia, its health is vital for regional ecosystems and economies. The Ganga serves millions who depend on it for agriculture, drinking water, and livelihoods.
When streamflow decreases, neighboring countries feel the repercussions too. Bangladesh relies heavily on cross-border water sharing with India. Reduced flow can lead to disputes over resources that could escalate into political tensions.
Moreover, a diminished Ganga compromises biodiversity within its watershed. Unique species face habitat loss due to changing water levels. This situation disrupts local fishing industries that many communities rely upon for sustenance.
Internationally, the plight of the Ganga raises alarms about climate resilience and sustainable practices worldwide. Observers look closely at how this river’s fate echoes larger patterns of environmental degradation across vulnerable regions globally.
Possible solutions and steps towards sustainability
To address the Ganga River crisis, a multi-faceted approach is essential. First, we must enhance water conservation techniques across agriculture. Implementing rainwater harvesting can significantly reduce dependency on river flow.
Another avenue lies in restoring wetlands along the riverbanks. These natural systems act as buffers, absorbing excess water during floods and releasing it slowly during dry spells. Community engagement plays a pivotal role, too. Educating local populations about sustainable practices ensures they understand their impact on this vital resource.
Additionally, investing in modern waste management systems can help alleviate pollution levels in the Ganga. Cleaner waters contribute to better streamflow and healthier ecosystems. Lastly, fostering international cooperation with neighboring countries like Bangladesh is crucial for equitable water-sharing agreements that benefit all parties involved while preserving this sacred river’s integrity.
Conclusion: Why we need to take action now for the future of the Ganga River.
The Ganga River, a lifeline for millions, faces an unprecedented crisis. With streamflow at alarmingly low levels, the implications extend far beyond its banks. Communities reliant on this sacred waterway are grappling with dwindling resources and shifting ecosystems.
Urgent action is required to address the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change and unsustainable practices. The proposed changes to the Ganges water-sharing treaty with Bangladesh signal a critical step towards collaborative management of this vital resource. However, more needs to be done.
Sustainability must become a priority in policymaking and community engagement alike. Innovative approaches that balance ecological health with human needs will be essential as we move forward.
Every moment counts for the future of the Ganga River and all those who rely on it. It’s time for individuals, communities, governments, and organizations worldwide to unite in safeguarding this irreplaceable treasure before it’s too late. Taking proactive steps today can ensure that future generations experience not just a river but an enduring legacy of hope and life flowing through their lands.


 Sports7 months ago
Sports7 months ago
 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months ago
 Apps7 months ago
Apps7 months ago
 Tech7 months ago
Tech7 months ago
 Entertainment7 months ago
Entertainment7 months ago
 Ganga Quest7 months ago
Ganga Quest7 months ago
 Ganga Quest7 months ago
Ganga Quest7 months ago
 Business7 months ago
Business7 months ago

1 Comment